Ans. Database - It is a collection of interrelated data. There can be stored in the form of tables. A database can be of any size and vary complexity. A database may be generated and manipulated manually or it may be computerized.
Database Management System (DBMS) →
1. it is collection of program that enable user to create and maintain a database.
2. In other word, it is general Purpose of Software that provide the user with the processes defining constructing and manipulating the database for various application.
Q.2 what is key and different type of key?
(or)
Discuss the candidate key, primary key, super key, composite key and alternate key.
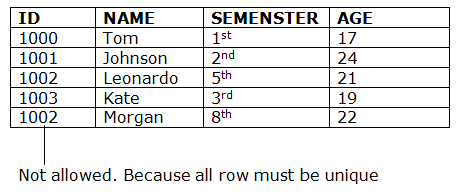
2. Key is defined for unique identification of rows in table. Consider the following example of an Employee table :Employee (Employee ID, Full Name, SSN, Dept ID)
Various types of keys are :
1. Primary key:
2. Super key:
3. Candidate key:
4. Composite key:
5. Alternate key:
6. Foreign key:
For example: Consider another table :
Q.3 Different between DBMS and RDBMS:
|
DBMS |
RDBMS |
|
1.DBMS application store data as file. |
1.RDBMS application store data in a
tabular form (table). |
|
2. Normalization is not present in the
DBMS. |
2.
Normalization present in the RDBMS |
|
3. DBMS does not support distributed
database. |
3. RDBMS support distributed database. |
|
4. Example of DBMS are file system XML
etc. |
4.
Example of RDBMS are my SQL or SQL server oracle etc. |
|
5. DBMS does not apply any security with
regart to data manipulation |
5. RDBMS define the integrity constant
for the purpose of ACID ( Automocity con sistency isolation and durability)
property. |
DBMS in Hindi – Integrity Constraints
- integrity constraints in dbms in hindi,
- Types of Integrity Constraint,
- Domain constraints,
- Entity integrity constraints,
- Referential Integrity Constraints,
- Key constraints,
- Types of Integrity Constraint,
Integrity Constraints in DBMS in Hindi
- Integrity constraints नियमों का एक समूह है। इसका उपयोग information की quality बनाए रखने के लिए किया जाता है।
- Integrity constraints यह सुनिश्चित करती है कि डेटा insertion, updating और अन्य प्रक्रियाओं को इस तरह से perform किया जाना चाहिए ताकि data integrity प्रभावित न हो।
- इस प्रकार, integrity constraint का उपयोग डेटाबेस को accidental damage से बचाने के लिए किया जाता है।
Types of Integrity Constraint
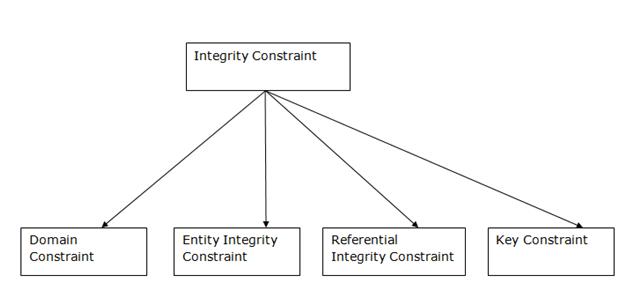
1. Domain constraints
- Domain constraints को एक attribute के लिए valid set of values की परिभाषा के रूप में परिभाषित किया जा सकता है।
- domain के data type में string, character, integer, time, date, currency आदि शामिल हैं। attribute की value संबंधित domain में उपलब्ध होनी चाहिए।
Example:
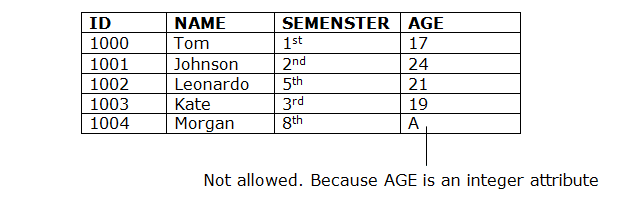
2. Entity integrity constraints
- Entity integrity constraint बताती है कि प्राथमिक key value, nullनहीं हो सकता है।
- ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि प्राथमिक key value का उपयोग संबंध में individual rows की पहचान करने के लिए किया जाता है और यदि प्राथमिक key की value null है, तो हम उन rows की पहचान नहीं कर सकते हैं।
- एक table में प्राथमिक key field के अलावा एक null value हो सकती है।
Example:
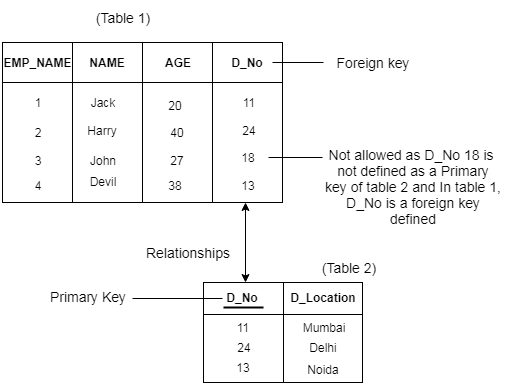
3. Referential Integrity Constraints
- एक referential integrity constraints दो तालिकाओं के बीच specified है।
- referential integrity constraints में, यदि तालिका 1 में एक foreign key तालिका 2 की प्राथमिक key को संदर्भित करती है, तो तालिका 1 में foreign key का प्रत्येक मान (value) null होना चाहिए या तालिका 2 में उपलब्ध होना चाहिए।
Example:
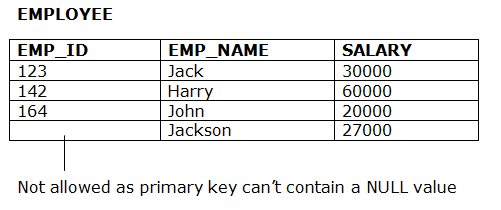
4. Key constraints
- Keys वह entity सेट है जिसका उपयोग किसी entity की विशिष्ट रूप से सेट की गई entity की पहचान करने के लिए किया जाता है।
- एक entity सेट में कई key हो सकती हैं, लेकिन इनमें से एक key प्राथमिक key होगी। एक प्राथमिक key में relational table में एक unique और null मान हो सकता है।
Example:
Relational algebra in DBMS in Hindi
Relational algebra एक procedural query भाषा है। यह query का परिणाम प्राप्त करने के लिए एक कदम दर कदम प्रक्रिया का इस्तेमाल करता है। यह प्रश्नों को करने के लिए operators का उपयोग करता है।एक operator या तो unary या binary हो सकता है । वे संबंधों को अपने इनपुट के रूप में स्वीकार करते हैं और उत्पादन के रूप में संबंधों को उपजते हैं। relational algebra को एक संबंध पर पुनरावर्ती रूप से किया जाता है और मध्यवर्ती परिणामों को भी संबंध माना जाता है।
Relational algebra के मूलभूत संचालन इस प्रकार हैं –
- Select
- Project
- Union
- Set different
- Cartesian product
- Rename
हम निम्नलिखित sections में इन सभी कार्यों पर चर्चा करेंगे।
Select Operation (σ)
यह tuples का चयन करता है जो किसी relation से दिए गए विधेय को संतुष्ट करते हैं।
Notation – σp(r)
जहाँ σ का चयन चयन के लिए होता है और r संबंध के लिए खड़ा होता है। p पूर्वसर्गीय तर्क (prepositional logic) formula है जो connectors जैसे की and, or, और not का उपयोग कर सकते हैं । ये relational operator का उपयोग कर सकते हैं जैसे − =, ≠, ≥, < , >, ≤।
उदाहरण के लिए –
- σsubject = “database”(Books)
Output – उन पुस्तकों से tuples का चयन करता है जहां subject ‘database’ है।
- σsubject = “database” and price = “450”(Books)
Output – उन पुस्तकों से tuples का चयन करता है जहां subject ‘डेटाबेस’ और ‘price’ 450 है।
- σsubject = “database” and price = “450” or year > “2010”(Books)
Output – उन पुस्तकों से tuples का चयन करता है जहां विषय ‘डेटाबेस’ और ‘price’450 है या 2010 के बाद प्रकाशित किताबें हैं।
Project Operation (∏)
यह column(s) को प्रोजेक्ट करता है जो किसी दिए गए विधेय को संतुष्ट करता है।
Notation − ∏A1, A2, An (r)
जहां A1, A2 , An संबंध r के attribute names हैं ।
Duplicate rows को automatically समाप्त कर दिया जाता है, क्योंकि संबंध एक set है।
उदाहरण के लिए –
- ∏subject, author (Books)
संबंध पुस्तकों से विषय और लेखक के नाम से columns को select करता है।
Union Operation (∪)
यह दो दिए गए संबंधों के बीच binary Union perform करता है और इसे इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया जाता है –
r ∪ s = { t | t ∈ r or t ∈ s}
Notation − r U s
जहाँ r और s या तो डेटाबेस संबंध या संबंध result set (temporary relation) हैं।
Union operation के मान्य होने के लिए, निम्नलिखित शर्तें पूरी होनी चाहिए –
- r , और s में बराबर attributes होने चाहिए।
- Attribute domain compatible होना चाहिए।
- Duplicate tuples automatically समाप्त हो जाते हैं।
∏ author (Books) ∪ ∏ author (Articles)
Output – उन लेखकों के नामों को प्रोजेक्ट करता है जिन्होंने या तो एक किताब या एक लेख या दोनों लिखा है।
Set Difference (−)
सेट-difference ऑपरेशन का परिणाम Tuples हैं, जो एक संबंध में मौजूद हैं, लेकिन दूसरे संबंध में नहीं हैं।
Notation − r − s
उन सभी tuples को ढूँढता है जो r में मौजूद हैं लेकिन s में नहीं ।
∏ author (Books) − ∏ author (Articles)
Output – उन लेखकों का नाम प्रदान करता है जिन्होंने किताबें लिखी हैं, लेकिन लेख नहीं।
Cartesian Product (Χ)
दो अलग-अलग संबंधों की जानकारी को एक में जोड़ता है।
Notation − r Χ s
जहां r और s संबंध हैं और उनके आउटपुट को इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया जाएगा –
r Χ s = { q t | q ∈ r and t ∈ s}
σauthor = ‘hinditutorialspoint’(Books Χ Articles)
Output – एक संबंध उत्पन्न करता है, जो hinditutorialspoint द्वारा लिखित सभी पुस्तकों और लेखों को दर्शाता है।
Rename Operation (ρ)
Relational algebra के परिणाम भी संबंध हैं लेकिन बिना किसी नाम के। Rename operation हमें आउटपुट relation का नाम बदलने की अनुमति देता है। ‘Rename’ ऑपरेशन छोटे Greek अक्षर rho ρ के साथ दर्शाया गया है ।
Notation − ρ x (E)
जहां x के नाम के साथ expression E का परिणाम save है ।
Additional operations are –
- Set intersection
- Assignment
- Natural join
Relational Calculus
Relational algebra के विपरीत, relational calculus एक non-procedural query भाषा है, अर्थात यह बताती है कि क्या करना है लेकिन यह कभी नहीं समझाता है कि यह कैसे करना है।
Relational calculus दो रूपों में मौजूद है –
Tuple Relational Calculus (TRC)
टुपल्स के ऊपर variable श्रेणियों को फ़िल्टर करना
Notation − {T | Condition}
सभी tuples T को लौटाता है जो शर्त को पूरा करता है।
उदाहरण के लिए –
{ T.name | Author(T) AND T.article = ‘database’ }
Output – लेखक से ‘नाम’ के साथ tuples लौटाता है जिसने ‘डेटाबेस’ पर लेख लिखा है।
TRC की मात्रा निर्धारित की जा सकती है। हम Existential (∃) और Universal Quantifiers (∀) का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए –
{ R| ∃T ∈ Authors(T.article=’database’ AND R.name=T.name)}
Output – उपरोक्त query पिछले वाले के समान परिणाम देगी।
SQL in dbms in hindi
- SQL का मतलब है structured query language इसका उपयोग relational database management system (RDMS) में डेटा को संग्रहीत करने और manage करने के लिए किया जाता है।
- यह रिलेशनल डेटाबेस सिस्टम के लिए एक standard language है। यह एक उपयोगकर्ता को रिलेशनल डेटाबेस और table बनाने, पढ़ने, अपडेट करने और delete में सक्षम बनाता है।
- SQL सभी RDBMS जैसे MySQL, Informix, Oracle, MS Access और SQL Server को अपनी standard डेटाबेस language के रूप में उपयोग करते हैं।
- SQL उपयोगकर्ताओं को कई तरह से अंग्रेजी जैसे statements का उपयोग करके डेटाबेस को query करने की अनुमति देता है।
SQL Rules in hindi:
SQL निम्नलिखित नियमों का पालन करता है:
- Structured query language, case sensitive नहीं है। आमतौर पर, SQL के keywords अपरकेस में लिखे जाते हैं।
- SQL की statements, text lines पर निर्भर हैं। हम एक या एक से अधिक text line पर एक single SQL statement का उपयोग कर सकते हैं।
- SQL statements का उपयोग करते हुए, आप एक डेटाबेस में अधिकांश क्रियाएं कर सकते हैं।
- SQL tuple relational calculus और relational algebra पर निर्भर करता है।
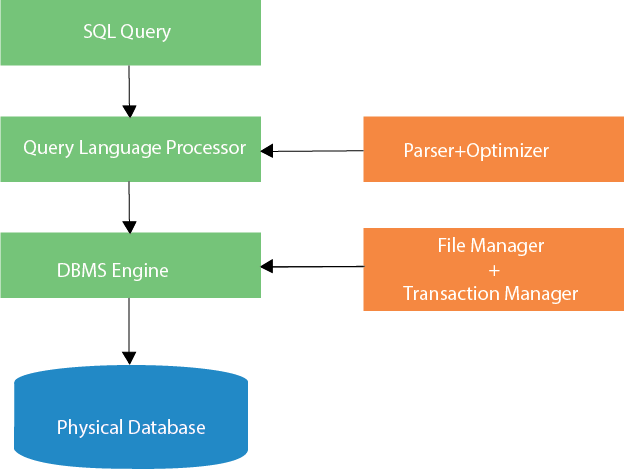
SQL process in hindi:
- जब कोई SQL कमांड किसी भी RDBMS के लिए निष्पादित होता है, तो सिस्टम request को पूरा करने का सबसे अच्छा तरीका बताता है और SQL इंजन निर्धारित करता है कि कार्य की व्याख्या कैसे करें।
- प्रक्रिया में, विभिन्न घटक शामिल हैं। ये घटक Optimisation engine query engine, query dispatcher, classic आदि हो सकते हैं।
- सभी non-SQL क्वेरी classic query इंजन द्वारा नियंत्रित की जाती हैं, लेकिन SQL क्वेरी इंजन logical फ़ाइलों को संभाल नहीं पाएगा।










0 Comments